Austin Water's annual consumer confidence report describes the overall quality of water from its raw collection and storage to the treated purity at your tap. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) requires that all drinking water suppliers provide a water quality report to their customers on an annual basis.
2024 Water Quality Report
Click on any report to view it as a larger, printable Adobe PDF file.
Do you need the free Adobe® Reader® for PDF files? Click here to download Adobe Reader.
Austin
- 2024 Water Quality Report
-
Español - 2024 Informe Anual Sobre la Calidad del Agua
Special Notice - You may be more vulnerable than the general population to certain microbial contaminants, such as Cryptosporidium, in drinking water. Infants, some elderly or immunocompromised persons such as those undergoing chemotherapy for cancer; those who have undergone organ transplants; those who are undergoing treatment with steroids; and people with HIV/AIDS or other immune system disorders can be particularly at risk from infections. You should seek advice about drinking water from your physician or health care provider. Additional guidelines on appropriate means to lessen the risk of infection by Cryptosporidium are available from the Safe Drinking Water Hotline at 800-426-4791.
En Español: Este reporte incluye información importante sobre el agua para tomar. Para asistencia en español, por favor llame al 512-972-0155.
About Your Water
- Where Your Drinking Water Comes From
-
Austin Water draws surface water from the Lower Colorado River as it flows through Lake Travis and Lake Austin. The water is then treated at a higher standard than what federal and state law requires at three specialized water treatment plants.

- We Protect the Source
-
TCEQ completed an assessment of our source water and results indicate that some of our sources are susceptible to certain contaminants. The sampling requirements for the water system are based on this susceptibility and previous sample data. Any detection of these contaminants will be found in this Consumer Confidence Report. For more information on source water assessments and protection efforts of our system, contact Austin Water’s Water Quality Manager at 512-972-0012.
- What Is in Your Drinking Water?
-
The sources of drinking water nationwide (both tap water and bottled water) include rivers, lakes, streams, ponds, reservoirs, springs and wells. As water travels over the surface of the land or through the ground, it dissolves naturally occurring minerals and, in some cases, radioactive material, and can be polluted by animals or human activity.
Contaminants that may be present in the source water include:
- Microbial contaminants, such as viruses and bacteria, which may come from sewage treatment plants, septic systems, agricultural livestock operations and wildlife.
- Inorganic contaminants, such as salts and metals, which can be naturally occurring or result from urban storm water runoff, industrial or domestic wastewater discharges, oil and gas production, mining or farming.
- Pesticides and herbicides, which may come from a variety of sources such as agriculture, storm water runoff and residential uses.
- Organic chemicals, including synthetic and volatile organic chemicals, which are byproducts of industrial processes and petroleum production and can also come from gas stations, urban storm water runoff and septic systems.
- Radioactive contaminants, which can be naturally occurring or the result of oil and gas production and mining activities.
In order to ensure that tap water is safe to drink, the EPA prescribes regulations which limit amounts of certain contaminants in water provided by public water systems. The Food and Drug Administration regulations establish limits for contaminants in bottled water which must provide the same protection for public health.
Contaminants may be found in drinking water that may cause taste, color or odor problems. These types of problems are not necessarily a cause for health concerns. For more information on taste, odor or color of drinking water, contact Austin Water at 512-972-0012.
Drinking water, including bottled water, may reasonably be expected to contain at least small amounts of some contaminants. The presence of contaminants does not necessarily indicate that the water poses a health risk. More information about contaminants and potential health effects can be obtained by calling the EPA’s Safe Drinking Water Hotline at 800-426-4791.
Our top priority is to ensure our water continues to be safe and satisfying to drink.
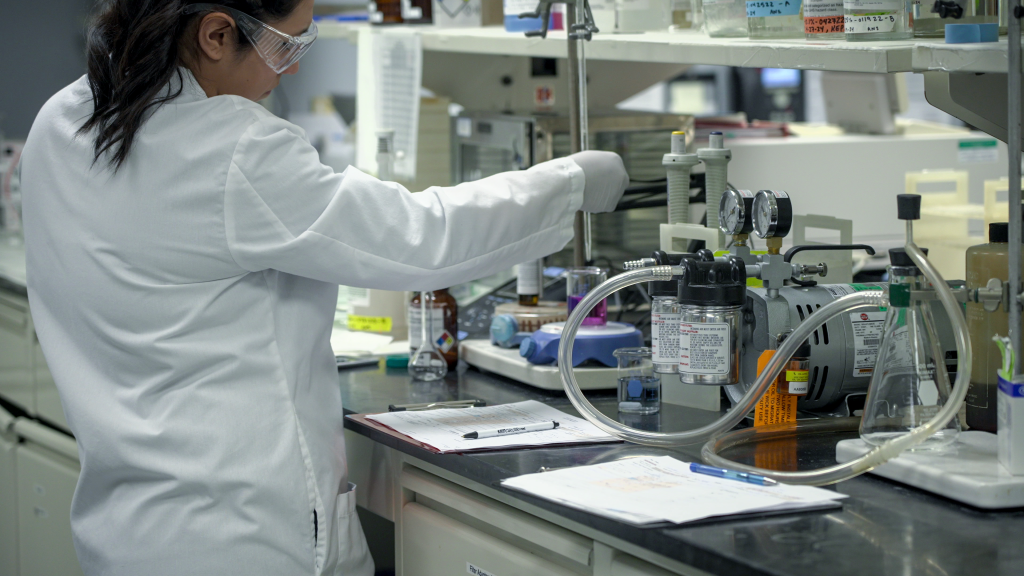

- Continuous Sampling and Testing
-
Austin Water collects samples at our treatment plants and across our water system multiple times a day, every day, to test for bacteria and chemicals that could pose a risk to our customers. Our top priority is to ensure our water continues to be safe and satisfying to drink.
We have taken steps to protect drinking water safety and quality that include:
Protecting Vital Infrastructure
- Following the devastating impacts of Winter Storm Uri in 2021, Austin Water’s infrastructure was repaired and
winterized to be more resilient during future extreme freezing weather events. - A copper sulfate feed system was installed in 2020 to protect raw water piping against zebra mussels that can damage equipment and affect taste and odor in drinking water.
- In 2016, Austin Water began a comprehensive record review and material inventory of all public water service lines,
including public and private side indicators, in compliance with the EPA’s Lead and Copper Rule Revisions. This work
was completed in October 2024 and confirmed that Austin’s public water system contains no lead pipes.
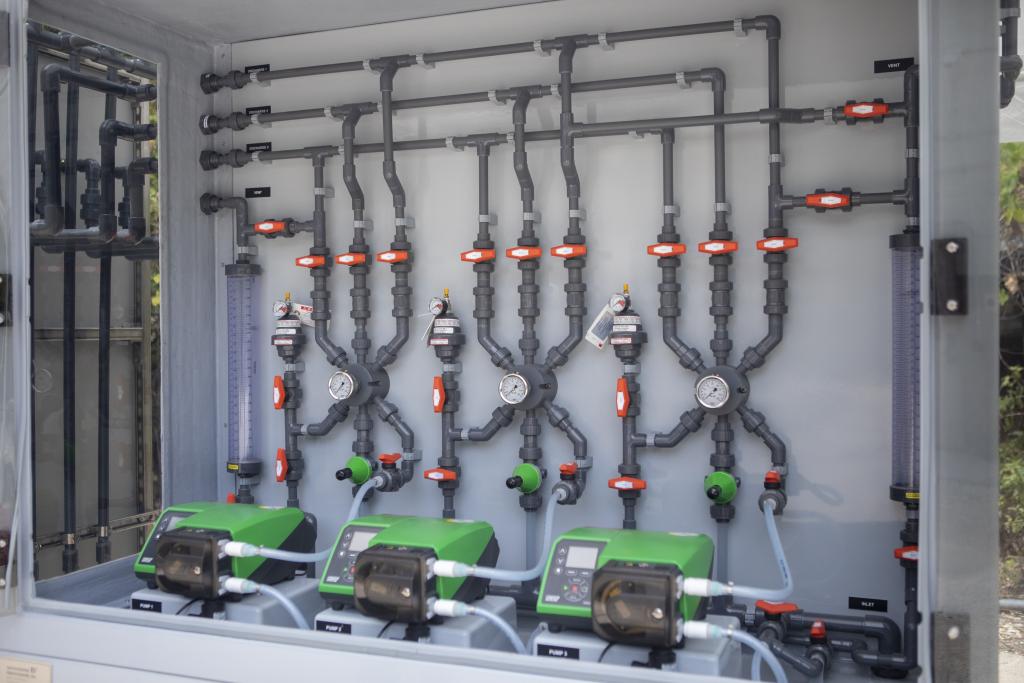

Pictured Above: Copper sulfate feed system

Pictured Above: Infrastructure winterization
Treatment Reliability
- Austin Water sets treatment goals and quality standards that are beyond the minimum state and federal regulatory
requirements to provide our customers superior water. TCEQ requirements call for 0.3 NTU or less in treated water or finished water clarity (turbidity), but Austin Water’s goal is 0.1 NTU or lower – and we consistently achieve this standard on average month after month, year after year. - Implementation of a polymer feed system began in 2020 to strengthen resiliency to flooding impacts and improve filter performance. This treatment capability is especially critical during events when high turbidity may occur in raw source water from the lakes. Polymer systems are now fully operational across all three water treatment plants.
- Powdered activated carbon is added as part of the treatment process to minimize taste and odor issues so that drinking water tastes fresh.
- In addition to using on-line equipment that continuously monitors treatment performance in real-time, licensed plant operators conduct water testing at least every two hours during multiple phases of the treatment process every day. This testing includes checks on the levels of disinfectant (chlorine/chloramine) residual, turbidity, pH, alkalinity and water softening.
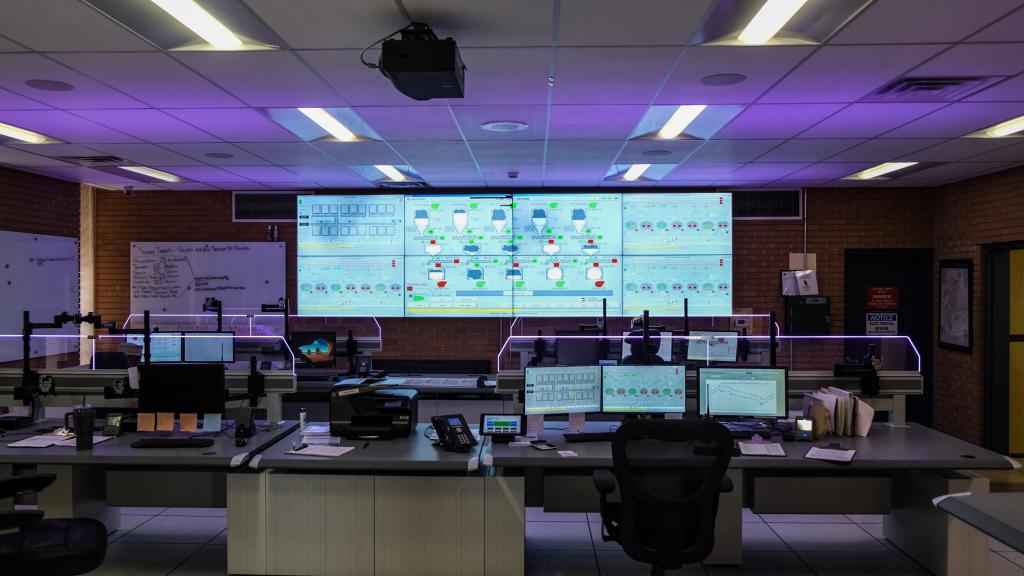

Pictured Above: Continuously monitored treatment performance
Quality Control in Storage, Pressure and Pipes
- Water storage tanks are tested routinely for bacteriological contaminants to ensure water remains at the same high quality as the moment it left the treatment plant.
- Water quality instrumentation, which provides real time monitoring for Austin Water operators, is installed and maintained in every major pressure zone to ensure water quality throughout the distribution system.
- Proactive water line replacement is underway, strengthening water distribution networks in 60 subdivisions. 90% of the polybutylene service water lines identified for replacement have been upgraded, as part of a capital improvement project that is helping to reduce line breaks and minimizing the risk of contaminant infiltration.

Pictured Above: Hands-on monitoring of total chlorine levels
Finished Drinking Water Testing
- For public safety, and to ensure Austin Water customers receive fresh water, annual maintenance is conducted on every fire hydrant in the city.
- In addition to daily testing at each water treatment plant, more than 300 water samples are collected each month to test for bacteriological contaminants, total chlorine residual levels and other important parameters throughout the water distribution system.
- In accordance with EPA’s Fifth Unregulated Contaminant Monitoring Rule, quarterly testing for PFAS was conducted from October 2023 to July 2024. The rule required drinking water providers, like Austin Water, to test for 29 specific PFAS chemicals – six of which will soon be regulated. Austin Water’s results revealed little to no detectable traces of PFAS in the City’s drinking water. For a complete list of sample results, please refer to the PFAS section below.
- Following the devastating impacts of Winter Storm Uri in 2021, Austin Water’s infrastructure was repaired and
Monitoring for Health Risks
- Cryptosporidium
-
Cryptosporidium is a parasite that can create an infection called gastroenteritis. Infection from Cryptosporidium organisms can occur in humans and animals and is spread by contact with soil, water, food or surfaces that have been contaminated. Austin Water monitors our lakes for Cryptosporidium because surface water sources are known to be susceptible to this contaminant.
During the 2024 monitoring for Cryptosporidium, Austin Water collected 20 samples. All samples reported no detection. The treatment processes employed at Austin Water’s treatment plants are effective for removal of Cryptosporidium.
- Harmful Algal Blooms
-
Cyanobacteria, also called blue-green algae, are microscopic organisms found naturally in surface waters. These organisms use sunlight to make their own food. In warm, nutrient rich waters, cyanobacteria can multiply quickly, creating algal blooms that spread across the water’s surface.
Some algae may produce cyanotoxins which can be harmful to humans and animals. Since 1992, Austin Water has monitored source water and drinking water for the presence of cyanobacteria. In 2015, Austin Water also began monitoring for the presence of cyanotoxins. We conduct routine testing for the presence of cyanotoxins in Lake Austin and Lake Travis, as well as in water that has finished the treatment process at the Handcox, Davis and Ullrich water treatment plants. Testing for the presence of cyanobacteria and other microscopic algae in raw lake water is conducted at least weekly, and cyanotoxin testing is performed on a routine basis. Sampling frequency is adjusted based on changing conditions.
In addition, to protect public health and safety, Austin Water has invested in leading-edge technology to shorten the time it takes to receive test results. Employing digital imaging particle analysis and same-day testing, we are able to detect harmful algae quicker than before. We also meet regularly with our counterparts at the City of Austin’s Watershed Protection Department and the Lower Colorado River Authority to review and report on our respective testing and mitigation approaches.
Austin Water performs several treatment techniques at our water plants to effectively and efficiently remove cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins. The harmful cells containing the toxins can be physically removed through the coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation and filtration process. Chlorine, which is part of the plant’s disinfection process, is destructive to cyanotoxins. Finally, the powdered activated carbon that is used to remove taste and odor causing compounds also removes cyanotoxins.
- Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS)
-
Testing and monitoring verified by the EPA concludes, Austin’s drinking water contains little to no traces of ‘forever chemicals’
In December 2024, Austin Water released results from a year’s worth of water quality testing as part of a nationwide effort by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to determine the presence of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in public drinking water. Austin Water’s results reveal little to no detectable traces of PFAS in the City’s drinking water. Because PFAS levels were either not detected or lower than EPA regulatory limits, no additional treatment to address these substances is required at this time.
Upcoming PFAS Regulations
Six PFAS compounds identified by the EPA will soon be regulated. The EPA is now working to determine how water utilities will have to test and treat drinking water.
The timeline for these regulations to take effect is:
- 2023 – 2027: Nationwide, water utilities are participating in the Fifth Unregulated Contaminant Monitoring Rules (UCMR 5) testing. Results will be used to determine requirements for testing, treatment, and future regulations.
- 2027 – 2029: Rules about sampling for PFAS and reporting results will go into effect.
- 2029 and beyond: Treatment processes that are required to remove PFAS from drinking water must be in place and working effectively.
Austin Water’s UCMR 5 results will be used to determine future requirements for testing. At this time, no treatment is required.
Because PFAS levels were either not detected or lower than EPA regulatory limits, no additional treatment to address these substances is required at this time.
Fifth Unregulated Contaminant Monitoring Rule (UCMR 5)
PFAS testing first began in October 2023 in accordance with the EPA’s Fifth Unregulated Contaminant Monitoring Rule (UCMR 5). The rule requires drinking water providers, like Austin Water, to measure the level of lithium – a metal/pharmaceutical - and 29 specific PFAS chemicals, six of which will soon be regulated. The quarterly tests were conducted over a 12-month period in treated tap water from all three water treatment plants.

UCMR 5 Test Results
UCMR 5 test results are shown in parts per trillion (ppt) in the table below. For reference, one ppt is equivalent to one drop in three Barton Springs Pools, or 1.2 square inches in the total area of Austin (305 square miles), or one cent in $10 billion.
Because testing for these chemicals involves trace amounts, some variation in samples from quarter to quarter can be expected. Some PFAS will be regulated using a unitless Hazard Index. The Hazard Index is computed using a formula for a mixture of four distinct PFAS. Austin’s Hazard Index ranges from 0.0 – 0.6 with an average Hazard Index of 0.2 for all four quarters.
*Asterisks indicate chemicals to be regulated in 2027 and the proposed limits set by the EPA.
Substance Highest
Level
Allowed*Austin Average
Q1
Q2
Q3
Q4
PFOA* 4.0 ppt
0
0
0
0
0
PFOS* 4.0 ppt
0.79
0
0 - 4.8
0
0
PFNA* 10 ppt
0
0
0
0
0
HFPO-DA (GenX)* 10 ppt
0
0
0
0
0
PFHxS* 10 ppt
2.3
0
0 - 6.2
0 - 4.8
0 - 4.0
PFBS* Not regulated individually
1.4
0
0 - 5.1
0 - 3.6
0
PFBA Not regulated
2.3
5.7 - 8.4
0
0
0 - 5.5
PFHxA Not regulated
0.5
0
0 - 3.3
0
0
PFPeA Not regulated
1.2
0
0 - 4.1
0 - 3.1
0
21 Other Compounds Not regulated
0
0
0
0
0
How Austin Water is Keeping the Lead Out
Austin Water Confirms No Lead Pipes in the System
After a comprehensive multi-year inspection conducted in compliance with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) guidelines, in October 2024, Austin Water announced that the city’s public water system is free of lead pipes. This milestone caps a decades-long effort to inventory and eliminate any lead infrastructure discovered in the system.
Austin Water has been proactively implementing many successful strategies to prevent exposure and get the lead out of our water for more than 50 years. Lead has not been permitted in public pipeline infrastructure since the 1950s, and Austin Water has removed any preexisting lead lines during normal maintenance activity and water line rehabilitation projects since the 1960s. In 2016, Austin Water began a comprehensive record review and material inventory of all public water service lines, as well as private side indicators, in compliance with EPA rules. This work confirmed that Austin’s public water system contains no lead pipes.
Austin Water’s detailed inventory included a comprehensive examination of public and private service line materials. Each line was categorized according to EPA requirements as lead, non-lead, galvanized requiring replacement (GRR), or lead status unknown.
Importantly, there are no unknown or lead service lines in the system inventory. In addition, Austin Water prioritized investigation of lines serving schools and licensed daycares. No lead pipes were found, but Austin Water actively encourages these entities to enroll in the state’s FREE voluntary program to receive free testing and free water filters where lead is found.
Austin Water’s lime softening process helps coat pipes and prevent corrosion that could leach lead into drinking water, even on the private side.
- Check Your Plumbing for Lead
-
Common sources of lead in drinking water include lead pipes, solder, and brass plumbing components like faucets, fixtures and pipe fittings. In Austin, lead pipes are less common than many other major cities across the United States because Austin stopped allowing lead pipe in private construction in 1967.
Galvanized iron or steel pipes that were previously downstream of lead pipe, known as “GRR”, may have adsorbed lead and present an increased risk of lead exposure. Homes built before 1986, when federal rules began requiring the use of “lead free” pipes and solder in water systems and facility plumbing, have long been considered most at risk. Fittings and fixtures were not included in these rules until 1996, with the most recent revisions to “lead free” being applied as late as 2014.
Your property’s build date can be found at your county’s property tax assessor. For information about properties in Travis County, visit the Travis Central Appraisal District.

- Sources of Lead in Drinking Water
-
If present, lead can cause serious health effects in people of all ages, especially pregnant people, infants (both formula-fed
and breastfed), and young children. In Austin, lead in drinking water is primarily from materials and parts used in service lines
and in home plumbing. Austin Water is responsible for providing high quality drinking water and removing lead pipes but cannot control the variety of materials used in the plumbing in your home.Because lead levels may vary over time, lead exposure is possible even when your tap sampling results do not detect lead at one point in time. You can help protect yourself and your family by identifying and removing lead materials within your home plumbing and taking steps to reduce your family’s risk. Using a filter, certified by an American National Standards Institute accredited certifier to reduce lead, is effective in reducing lead exposures. Follow the instructions provided with the filter to ensure the filter is used properly.
Use only cold water for drinking, cooking, and making baby formula. Boiling water does not remove lead from water. Before
using tap water for drinking, cooking, or making baby formula, flush your pipes for several minutes. You can do this by running your tap, taking a shower, doing laundry or a load of dishes. If you have a lead service line or galvanized requiring replacement service line, you may need to flush your pipes for a longer period.If you are concerned about lead in your water and wish to have your water tested, contact Austin Water at 512-972-2133.
Information on lead in drinking water, testing methods, and steps you can take to minimize exposure is available at www.epa.gov/safewater/lead.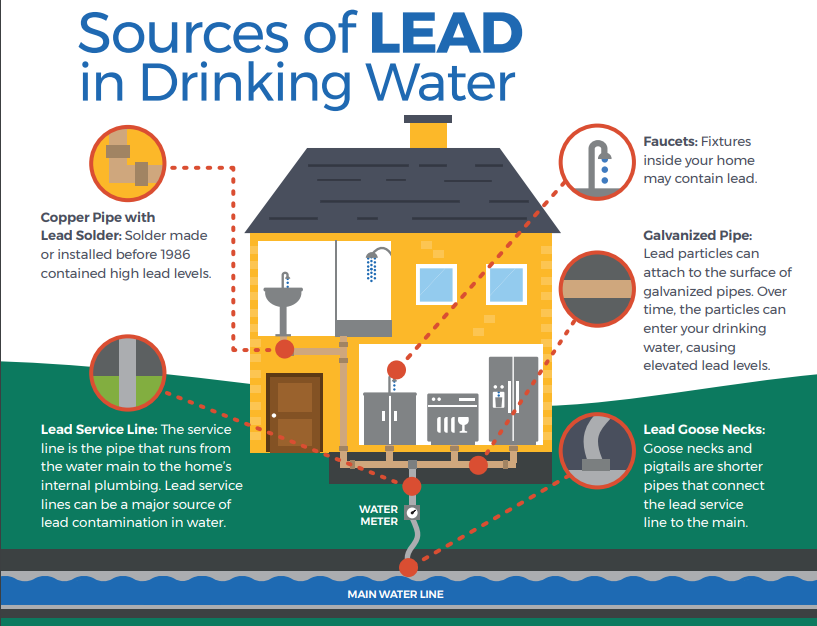
Fluoride
- Drinking Water Fluoridation
-
In 1945, municipalities began adding fluoride to drinking water to fight tooth decay. Follow up studies in these communities over 13-15 years showed a 50-70% reduction in cavities.
Because of the potential public health benefits to residents, the City of Austin held a public vote on fluoridation in the early 1970s. The referendum passed with the support of the community, and Austin Water began adding fluoride to the water on February 2, 1973.
On December 15, 2011, Austin City Council voted to continue fluoridating, in accordance with public health recommendations from the Centers for Disease Control and the City’s Health and Human Services Department. Austin Water must follow the current fluoridation policies until they are changed or no longer in place.
Austin Water’s fluoridation is done in accordance with local and national public health agencies and the American Water Works Association (AWWA). AWWA supports the recommendations of the World Health Organization (WHO), American Medical Association (AMA), American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), Canadian Medical Association (CMA), Centers for Disease Control (CDC), American Dental Association (ADA), and Canadian Dental Association (CDA), for the fluoridation of public water supplies as a public health benefit.
Austin Water will closely monitor the Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA’s) response to a recent federal court ruling in California. The ruling does not require immediate changes to any water system’s fluoridation practices, and it does not overrule the EPA’s existing drinking water standards for fluoride.
The EPA has appealed this ruling. Austin Water will also continue to coordinate with the Austin Public Health Department, as we have always done regarding fluoridation of Austin’s drinking water, to ensure the protection of public health.
- Fluoride and Infants
-
Water fluoridated at a level optimal for oral health, as is used in Austin, poses no known health risks for infants. However, some children may develop enamel fluorosis, a cosmetic condition where faint white markings or streaks may appear on the teeth. If you’re concerned about fluorosis, you can minimize your baby’s exposure by breastfeeding or using ready-to-feed formula. You can also alternate or mix tap water and non-fluoridated water when preparing infant formula. If you use only non-fluoridated water, such as purified, deionized or distilled water to prepare your baby’s formula, your doctor may recommend fluoride supplements.
Consumer Confidence Report
Stay Informed About Your Water
- Monthly Board and Commission Meetings
-
There are many opportunities for public input and participation on issues and topics related to water quality. Attend an Austin City Council or Water & Wastewater Commission meeting to learn more.
Meeting agendas, dates and times can be found by visiting the Water & Wastewater Commission webpage or the Austin City Council Meeting Information Center webpage.
- Social Media
-
Follow Austin Water on Facebook, X (Twitter) and Instagram for information about water quality, updates about infrastructure improvements we’re making to be more resilient, fun lessons for students or opportunities to get involved with water planning in our community. We also share helpful tips on conservation, landscaping and how to protect your pipes during extreme weather events.
- Infrastructure Investments
-
Austin Water continues to make strategic investments in infrastructure improvements to strengthen the water distribution system, proactively replace water lines and reduce the number of line breaks and the risk of infiltrating contaminants.
Water Loss
The American Water Works Association and Texas Water Development Board establish industry standards for water loss, known as the Infrastructure Leak Index or ILI. Water loss is a function of leakage from the mains and fixtures and a utility’s ILI is scaled to take into account the number of connections and the miles of mains in the system. ILI is not affected by water use or population, which varies from city to city.
For a utility the size of Austin Water, an ILI of between 3 and 5 is considered appropriate.
Austin Water is working to complete our 2024 Water Loss Audit and ILI for the Texas Water Development Board. This information will be available in May and posted in the Managing Water Loss section of the System Maintenance webpage.
Current Water Quality Results
Visit our monthly and quarterly summaries for the most up-to-date water quality results such as total hardness, pH, total (dissolved) solids, and more.
Archived Reports
Annual water quality reports from previous years can be viewed below.
Resources
A list of frequently asked questions is available.


