An introduction to the Land Development Code (LDC) and related information.
What is the Land Development Code?
The the rules and processes that regulate where and what type of development may occur. The Code has a significant impact on our daily life, from shaping the kinds of places where we live, work, and shop, as well as influencing the design of our streets and public spaces.
Types of Zoning Codes
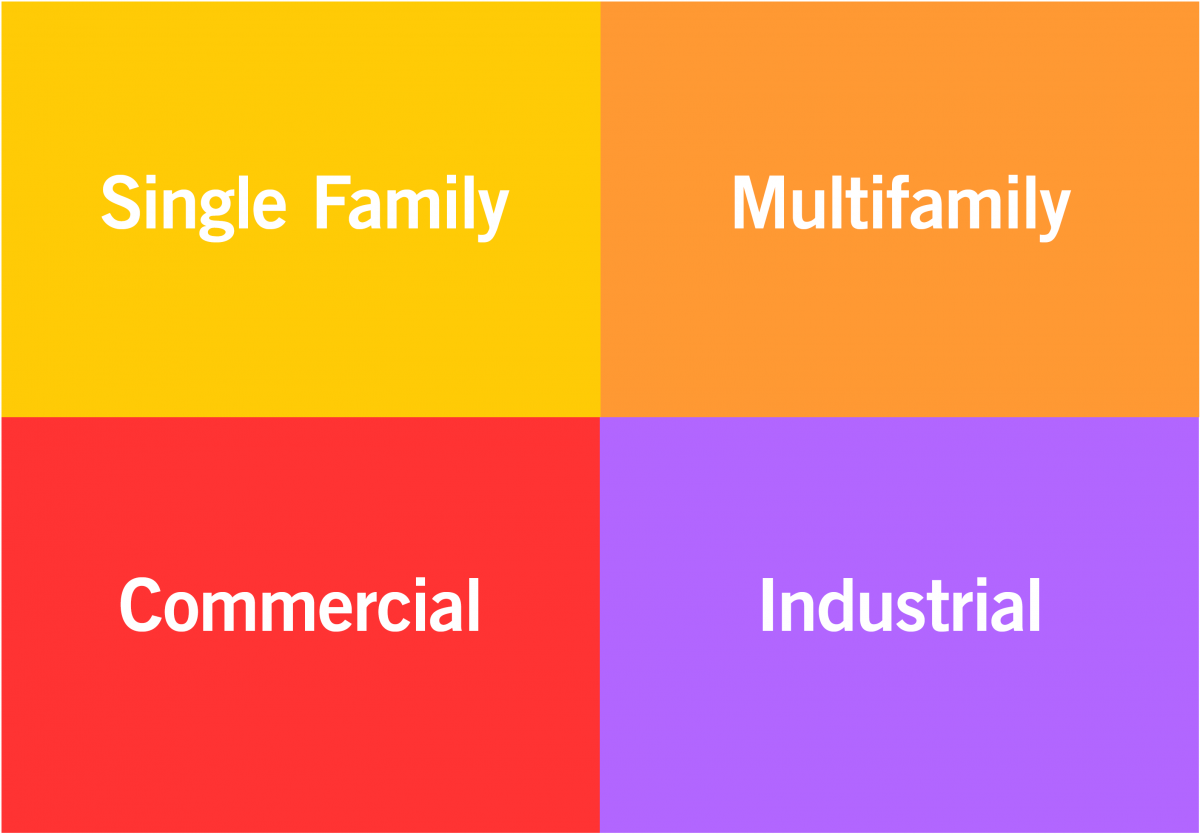 Euclidean Zoning
Euclidean Zoning
This type of zoning separates different land uses and concentrates similar land uses into distinct areas or zones. For example, single-family housing is concentrated in one area, multi-family in another, retail uses in another, and industrial uses in another.
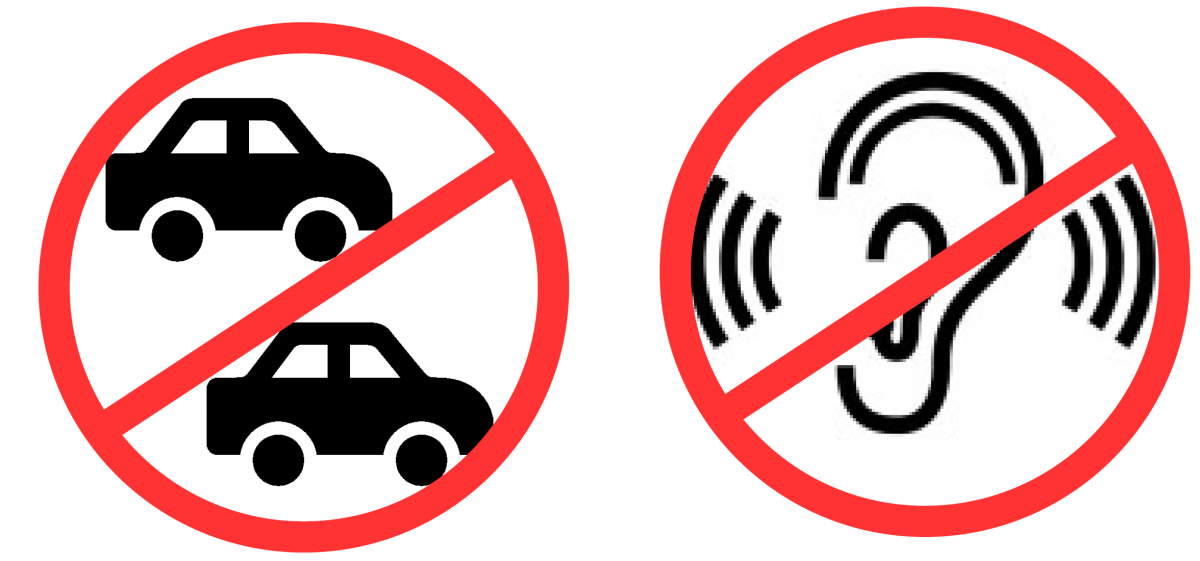 Performance Zoning
Performance Zoning
Performance zoning regulates the effects or impact of land uses on surrounding properties through performance standards. Key elements of Performance zoning include number of vehicle trips, density or noise levels.
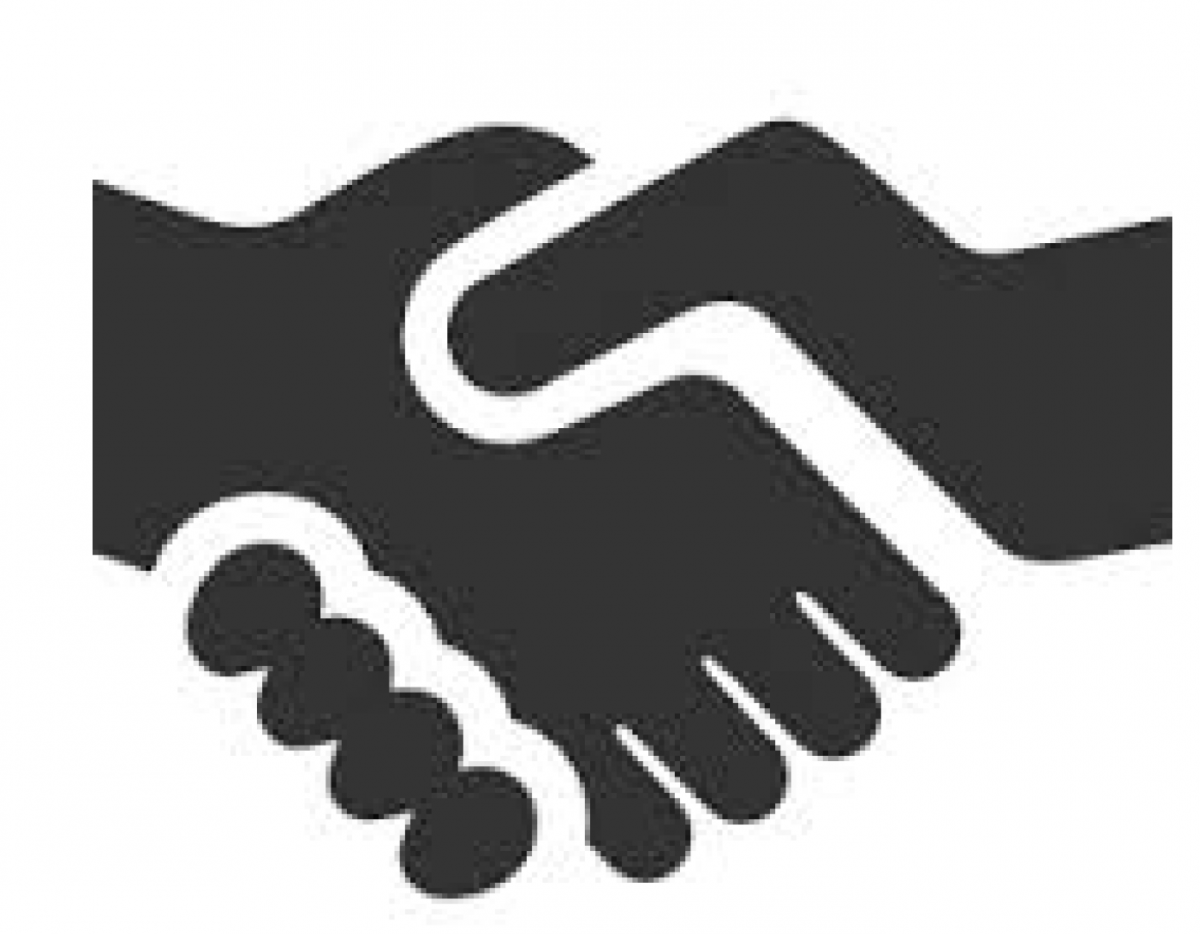 Negotiated Zoning
Negotiated Zoning
Negotiated zoning evolved out of the perceived rigidity of Euclidean zoning and allows landowners to vary uses and development standards in a zoning ordinance through a negotiated process. When approved, this type of zoning becomes a “mini-zoning ordinance” that regulates development of the site.
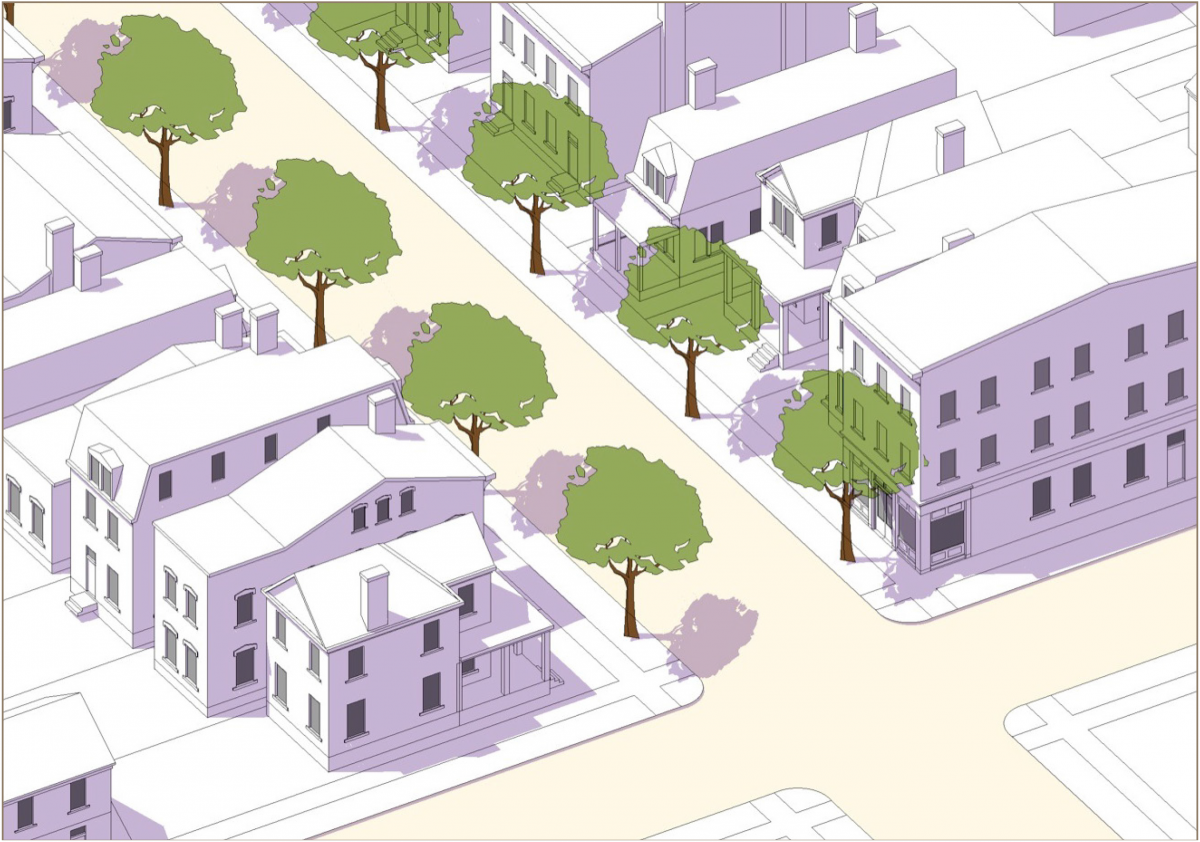 Form-Based Code
Form-Based Code
Form-Based Codes are a zoning tool that utilize a community’s unique characteristics of walkable urban development patterns, or the existing DNA of a place, as the framework for
a code to foster compatible, predictable, high-quality built results.
 Hybrid Zoning
Hybrid Zoning
The term “hybrid code” generally refers to zoning regulations that combine various aspects of all the zoning models discussed above. There are hundreds of approaches to combining different types of zoning codes. In fact, it is safe to say that no two hybrid zoning systems are the same.
